

- PYTHON INTERPRETER PYCHARM HOW TO
- PYTHON INTERPRETER PYCHARM CODE
- PYTHON INTERPRETER PYCHARM DOWNLOAD
Let’s say you have a class that declares a method and that method is being used inside the class at different points. The final decorator prohibits any class decorated with from being subclassed, and any method decorated with from being overridden in a subclass. If needed, this feature will let you declare that a method should not be overridden, that a class should not be subclassed, or that a variable or attribute should not be reassigned. With this new version, a final decorator and a `Final` type annotation are introduced to help restrict the usage of methods, classes, and variables. When you design a class, you have to make sure your methods are used properly. The ‘after’ loop has the assignment inside its control statement definition by using an assignment expression. In the previous example, the ‘before’ while loop has a variable assignment before it and also inside its execution code. When you use this feature, the loop’s control expression will also hold the variable definition and reassignment. One example of such usage can be a while loop with a control variable. For example, comma-separated assignments with the equals operator are not the same as the ones made by the walrus operator. An important note is that the walrus operator is different from the equals operator. The syntax to declare a variable consists of the walrus operator `:=` inside an expression enclosed by parentheses.

PYTHON INTERPRETER PYCHARM CODE
As a result, you can make your code less verbose and add compactness, as declarations can be made within expressions in the same line. Now, expressions can also assign values as part of their declaration, which removes the necessity to initialize variables in advance. Assignment expressionsĪ new way to assign values to variables is available with this latest Python version. One of the advantages of positional-only parameters is that, if you decide to change the variable names in the function definition, your library’s users won’t be affected as there are no keyword dependencies in the function calls they make to begin with. In the past, if you renamed the arguments of your function for refactoring purposes (or any other reason), the code of your library’s users would be at risk if they were to make a function call with keyword arguments (for example, `select_random(a=3, b=89, c=54)`). By design, you decide that those arguments should be positional-only:īy doing this, you ensure that your library’s users won’t be able to call your function with the arguments’ keywords. The semantic meaning stays the same, regardless of the order of the values in the function call. Such values can be passed in any position and the function will return you a random choice. Say, you have a function in your library that selects a value randomly from different values passed as arguments. This is closely analogous to the keyword-only arguments syntax, but instead of setting the arguments after the asterisk`*`, you do it before the slash`/`. To use this feature, just set the arguments in your function definition and write a forward slash`/` after the last positional-only argument you want to declare. As of now, Python only had the option to define arguments as positional, keyword, or keyword-only, but with this new version we now have another way to define them by using positional-only parameters.
One way to achieve such explicitness is by how the function can be called with its arguments. The more explicit these definitions are, the easier they are to implement.

Positional-only parametersįunction definitions are a key element when designing libraries and APIs for user consumption.
PYTHON INTERPRETER PYCHARM HOW TO
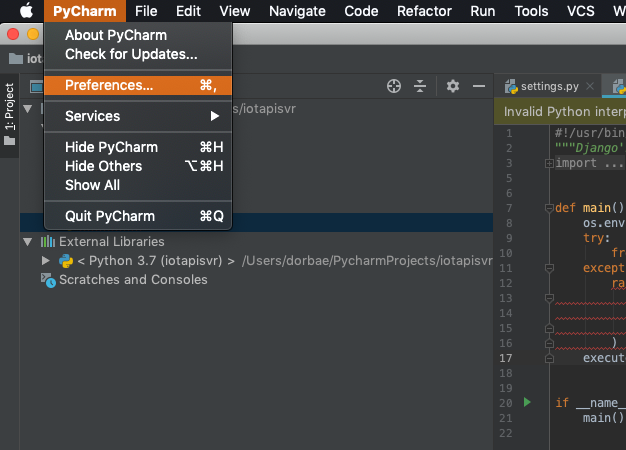
From there you will just need to switch to Python 3.8 as your interpreter in P圜harm (if you’re not sure how to switch the interpreter, jump into our documentation for help).
PYTHON INTERPRETER PYCHARM DOWNLOAD
To try them out, get the latest version of P圜harm and download the current beta release of Python 3.8 from here. This article will walk you through the features currently supported by our latest P圜harm release. Of course, P圜harm couldn’t get behind, so we now support some of the major features coming with this new version. From new ways of assigning expressions to restriction of usage of function declarations, calls, and variable assignations, this latest release presents new options to code. The language is evolving according to its community’s needs by addressing cases where new syntax or logic become necessary. The release of Python 3.8 brought new features to the Python coding realm.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
